Business Analyst: Difference between revisions
Created page with "Thao Lan NGUYEN THI organized 2 training sessions about the job of '''Business Analyst''' (also known as "BA") in IT Development in May 2016 and April 2017. == Session 1 == =..." |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:BA-is-a-skill.jpg]] | |||
Thao Lan NGUYEN THI organized 2 training sessions about the job of '''Business Analyst''' (also known as "BA") in IT Development in May 2016 and April 2017. | Thao Lan NGUYEN THI organized 2 training sessions about the job of '''Business Analyst''' (also known as "BA") in IT Development in May 2016 and April 2017. | ||
| Line 10: | Line 12: | ||
Job titles for business analysis practitioners include not only business analyst, but also business systems analyst, systems analyst, requirements engineer, process analyst, product manager, product owner, enterprise analyst, business architect, management consultant, business intelligence analyst, data scientist, and more. Many other jobs, such as management, project management, product management, software development (dev), quality assurance (test/QC) and interaction design (UI/ UX design) rely heavily on business analysis skills for success. | Job titles for business analysis practitioners include not only business analyst, but also business systems analyst, systems analyst, requirements engineer, process analyst, product manager, product owner, enterprise analyst, business architect, management consultant, business intelligence analyst, data scientist, and more. Many other jobs, such as management, project management, product management, software development (dev), quality assurance (test/QC) and interaction design (UI/ UX design) rely heavily on business analysis skills for success. | ||
[[File:BA-is-not-a-single-person.jpg]] | |||
'''To remember :''' | '''To remember :''' | ||
| Line 116: | Line 120: | ||
*Enterprise Architect | *Enterprise Architect | ||
|} | |} | ||
[[File:You-dont-need-IT-knowledge-to-be-BA.jpg]] | |||
==Session 3== | |||
===Requirements Engineering=== | |||
====Definition of “Requirement”==== | |||
(Based on IEEE 610.12-1990: IEEE Standard Glossary of Software Engineering Terminology) | |||
#A condition or capability needed by a stakeholder to solve a problem or achieve an objective | |||
#A condition or capability that must be met or possessed by a solution or solution component to satisfy a contract, standard, specification, or other formally imposed documents. | |||
#A documented representation of a condition or capability as in (1) or (2). | |||
====Classification==== | |||
*Business Requirements | |||
*Stakeholder Requirements | |||
*Solution Requirements (Functional / Non-functional) | |||
* Transition Requirements | |||
===Requirements Engineering Good Practices=== | |||
More than 50 practices, grouped into 7 categories. | |||
{| class="wikitable" | |||
|- | |||
| '''Elicitation''' | |||
|| | |||
Define vision and scope, Identify user classes, Select product champions, Conduct focus groups, Identify user requirements, Identify system events and responses, Hold elicitation interviews, Hold facilitated elicitation workshops, Observe users performing their jobs, Distribute questionnaires, Perform document analysis, Examine problem reports, Reuse existing | |||
|- | |||
| '''Analysis''' | |||
|| | |||
Model the application environment, Create prototypes, Analyze feasibility, Prioritize requirements, Create a data dictionary, Model the requirements, Analyze interfaces, Allocate requirements to subsystems | |||
|- | |||
| '''Specification''' | |||
|| Adopt requirement document templates, Identify requirement origins, Uniquely label each requirement, Record business rules, Specify non-functional requirements | |||
|- | |||
| '''Validation''' | |||
|| Review the requirements, Test the requirements, Define acceptance criteria, Simulate the requirements | |||
|} | |||
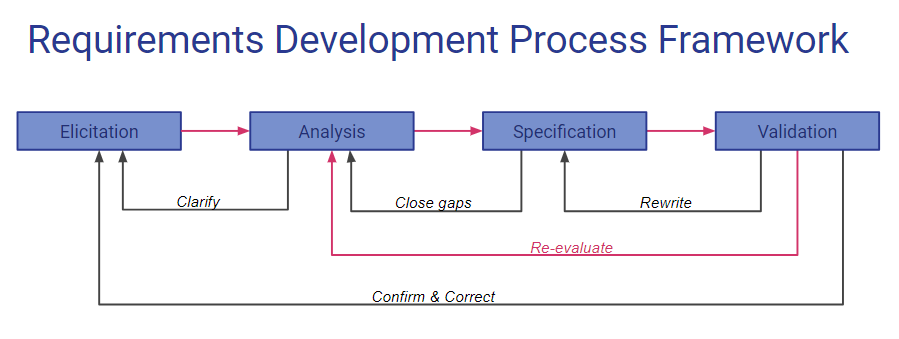
===Requirements Development Process Framework=== | |||
[[File:Requirements Development Process Framework.PNG]] | |||
{| class="wikitable" | |||
|- | |||
| '''Requirement Management''' | |||
|| Establish a change control process, Perform change impact analysis, Establish baselines and control versions of requirements sets, Maintain change history, Track requirements status, Track requirements issues, Maintain a requirements traceability matrix, Use a requirements management tool | |||
|- | |||
| '''Knowledge''' | |||
|| Train business analysts, Educate stakeholders about requirements, Educate developers about application domain, Define a requirements engineering process, Create a glossary | |||
|- | |||
| '''Project Management''' | |||
|| Select an appropriate life cycle, Plan requirements approach, Estimate requirements effort, Base plans on requirements, Identify requirements decision makers, Renegotiate commitments, Manage requirements risks, Track requirements effort, Review past lessons learned | |||
|} | |||
=== Sources === | |||
* [https://lostechies.com/joeocampo/2007/09/20/agile-vs-traditional-development-cost-models-maybe/ “Traditional Methodology Resource Cost” Chart] | |||
* BABOK v2.0 | |||
* Microsoft.Press.Software.Requirements.3.3rd.Edition.Aug.2013.pdf | |||
* [https://www.slideshare.net/MarrajuBollapRagada/agile-vs-iterativevswaterfall Quick understanding about Waterfall / Iterative / Agile] | |||
Revision as of 06:22, 30 January 2018
Thao Lan NGUYEN THI organized 2 training sessions about the job of Business Analyst (also known as "BA") in IT Development in May 2016 and April 2017.
Session 1
What is Business Analysis?
Business Analysis is the practice of enabling change in an organizational context, by defining needs and recommending solutions that deliver value to stakeholders. (IIBA definition)
What is a Business Analyst?
Job titles for business analysis practitioners include not only business analyst, but also business systems analyst, systems analyst, requirements engineer, process analyst, product manager, product owner, enterprise analyst, business architect, management consultant, business intelligence analyst, data scientist, and more. Many other jobs, such as management, project management, product management, software development (dev), quality assurance (test/QC) and interaction design (UI/ UX design) rely heavily on business analysis skills for success.
To remember :
- BA as a skill
- BA is not only a single person.
Session 2
What’s my career path in BA?
| Business Focused | IT focused |
|---|---|
|
|
Decision Analyst
Often referred to as a Business Intelligence Analyst
| Input | Output |
|---|---|
| Data & Statistical Methods | The ability to gain insight and to drive business planning |
Business analysis job profiles
| Project/ IT Executes projects | Transition/ Functional Guides projects | Enterprise/ Strategic Creates projects | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Generalist |
|
|
|
| Specialist |
|
|
|
| Hybrid |
|
|
|
Session 3
Requirements Engineering
Definition of “Requirement”
(Based on IEEE 610.12-1990: IEEE Standard Glossary of Software Engineering Terminology)
- A condition or capability needed by a stakeholder to solve a problem or achieve an objective
- A condition or capability that must be met or possessed by a solution or solution component to satisfy a contract, standard, specification, or other formally imposed documents.
- A documented representation of a condition or capability as in (1) or (2).
Classification
- Business Requirements
- Stakeholder Requirements
- Solution Requirements (Functional / Non-functional)
- Transition Requirements
Requirements Engineering Good Practices
More than 50 practices, grouped into 7 categories.
| Elicitation |
Define vision and scope, Identify user classes, Select product champions, Conduct focus groups, Identify user requirements, Identify system events and responses, Hold elicitation interviews, Hold facilitated elicitation workshops, Observe users performing their jobs, Distribute questionnaires, Perform document analysis, Examine problem reports, Reuse existing |
| Analysis |
Model the application environment, Create prototypes, Analyze feasibility, Prioritize requirements, Create a data dictionary, Model the requirements, Analyze interfaces, Allocate requirements to subsystems |
| Specification | Adopt requirement document templates, Identify requirement origins, Uniquely label each requirement, Record business rules, Specify non-functional requirements |
| Validation | Review the requirements, Test the requirements, Define acceptance criteria, Simulate the requirements
|
Requirements Development Process Framework
| Requirement Management | Establish a change control process, Perform change impact analysis, Establish baselines and control versions of requirements sets, Maintain change history, Track requirements status, Track requirements issues, Maintain a requirements traceability matrix, Use a requirements management tool |
| Knowledge | Train business analysts, Educate stakeholders about requirements, Educate developers about application domain, Define a requirements engineering process, Create a glossary
|
| Project Management | Select an appropriate life cycle, Plan requirements approach, Estimate requirements effort, Base plans on requirements, Identify requirements decision makers, Renegotiate commitments, Manage requirements risks, Track requirements effort, Review past lessons learned |
Sources
- “Traditional Methodology Resource Cost” Chart
- BABOK v2.0
- Microsoft.Press.Software.Requirements.3.3rd.Edition.Aug.2013.pdf
- Quick understanding about Waterfall / Iterative / Agile